What is WorkManager?
WorkManager is one of the Android Architecture Components and part of Android Jetpack, a new and opinionated take on how to build modern Android applications.
WorkManager is an Android library that runs deferrable background work when the work’s constraints are satisfied.
WorkManager is intended for tasks that require a guarantee that the system will run them even if the app exits.
In other words, WorkManager provides a battery-friendly API that encapsulates years of evolution of Android’s background behavior restrictions. This is critical for Android applications that need to execute background tasks!
When to use WorkManager
WorkManager handles background work that needs to run when various constraints are met, regardless of whether the application process is alive or not. Background work can be started when the app is in the background, when the app is in the foreground, or when the app starts in the foreground but goes to the background. Regardless of what the application is doing, background work should continue to execute, or be restarted if Android kills its process.
A common confusion about WorkManager is that it’s for tasks that needs to be run in a “background” thread but don’t need to survive process death. This is not the case. There are other solutions for this use case like Kotlin’s coroutines, ThreadPools, or libraries like RxJava. You can find more information about this use case in the guide to background processing.
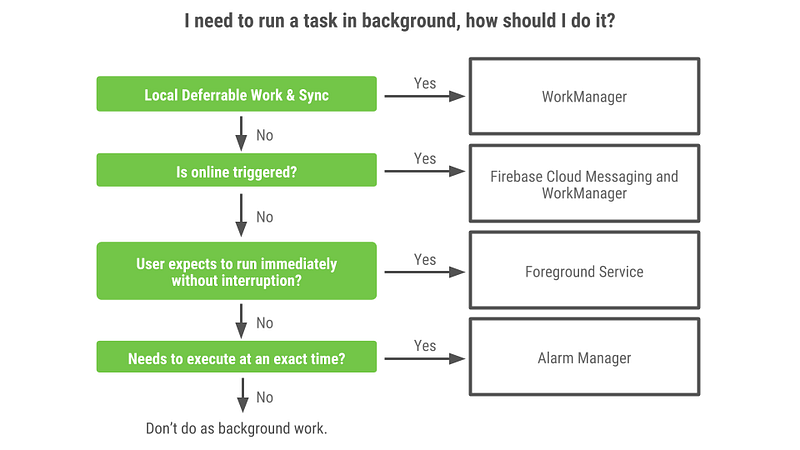
There are many different situations in which you need to run background work, and therefore different solutions for running background work. This blog post about background processing provides a lot of great information about when to use WorkManager. Take a look at this diagram from the blog:
In the case of WorkManager, it’s best for background work that has to finishand is deferrable.
To start, ask yourself:
- Does this task need to finish?
If the application is closed by the user, is it still necessary to complete the task? An example is a note taking application with remote sync; once you finish writing a note, you expect that the app is going to synchronize your notes with a backend server. This happens even if you switch to another app and the OS needs to close the app to reclaim some memory. It also should happen even if you restart the device. WorkManager ensures tasks finish. - Is this task deferrable?
Can we run the task later, or is it only useful if run right now? If the task can be run later, then it’s deferrable. Going back to the previous example, it would be nice to have your notes uploaded immediately but, if this is not possible and the synchronization happens later, it’s not a big problem. WorkManager respects OS background restrictions and tries to run your work in a battery efficient way.
So, as a guideline, WorkManager is intended for tasks that require a guarantee that the system will run them, even if the app exits. It is not intended for background work that requires immediate execution or requires execution at an exact time. If you need your work to execute at an exact time (such as an alarm clock, or event reminder), use AlarmManager. For work that needs to be executed immediately but is long running, you’ll often need to make sure that work is executed when in the foreground; whether that’s by limiting execution to the foreground (in which case the work is not longer true background work) or using a Foreground Service.
WorkManager can and should be paired with other APIs when you need to trigger some background work in more complex scenarios:
- If your server triggers the work, WorkManager can be paired with Firebase Cloud Messaging.
- If you are listening for broadcasts using a broadcast receiver and then need to trigger long running work, you can use WorkManager. Note that WorkManager provides support for many common Constraints that normally come through as broadcasts — in these cases, you don’t need to register your own broadcast receivers.
Why use WorkManager?
WorkManager runs background work while taking care of compatibility issues and best practices for battery and system health for you.
Furthermore, using WorkManager, you can schedule both periodic tasks and complex dependent chains of tasks: background work can be executed in parallel or sequentially, where you can specify an execution order. WorkManager seamlessly handles passing along input and output between tasks.
You can also set criteria on when the background task should run. For example, there’s no reason to make an HTTP request to a remote server if the device doesn’t have a network connection. So you can set a Constraint that the task can only run when a network connection is present.
As part of guaranteed execution, WorkManager takes care of persisting your work across device restarts and if your process is force-stopped. You can also easily define retry strategies if your work is stopped and you want to retry it later.
Finally, WorkManager lets you observe the state of the work request so that you can update your UI.
To summarize, WorkManager offers the following benefits:
- Handles compatibility with different OS versions
- Follows system health best practices
- Supports asynchronous one-off and periodic tasks
- Supports chained tasks with input/output
- Lets you set constraints on when the task runs
- Guarantees task execution, even if the app or device restarts
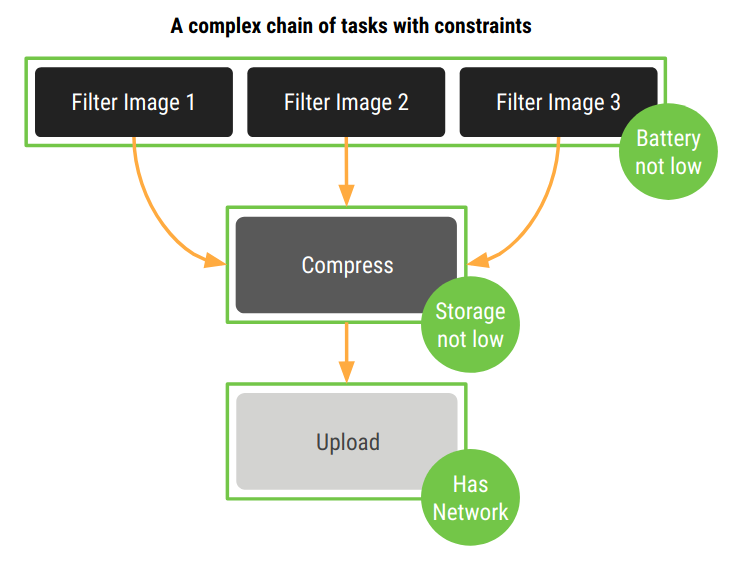
Let’s see a concrete example where we build a pipeline of concurrent tasks that applies filters to an image. The result is then sent to a compress task and then to an upload task.
We can define a set of constraints for these tasks and specify when they can be executed:
All these workers define a precise sequence: e.g. we don’t know the order in which the images will be filtered, but we know that the Compress worker will start only after all the Filter workers have completed.
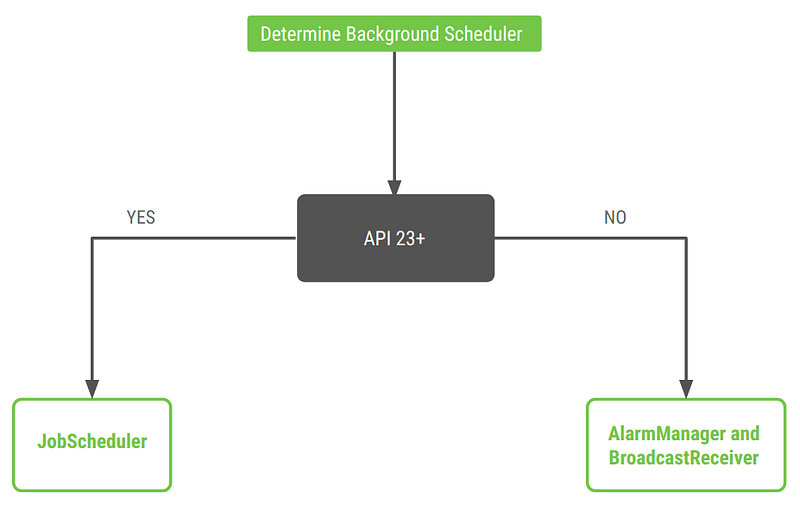
How the WorkManager scheduler works
To ensure compatibility back to API level 14, WorkManager chooses an appropriate way to schedule a background task depending on the device API level. WorkManager might use JobScheduler or a combination of BroadcastReceiver and AlarmManager.
Is WorkManager ready for production use?
WorkManager is now in beta. This means that there will be no breaking API changes in this major revision.
Comments
Post a Comment